When your blood starts clotting too much, it can block arteries and trigger a heart attack or stroke. That’s where antiplatelet drugs, medications that stop blood platelets from sticking together and forming dangerous clots. Also known as anti-clotting agents, they’re one of the most common long-term treatments after a heart procedure or stroke. Unlike blood thinners like warfarin that affect clotting factors, antiplatelet drugs target the platelets—tiny cells in your blood that act like first responders when there’s damage to a blood vessel.
Two of the most used antiplatelet drugs are ticagrelor, a fast-acting drug often prescribed after stent placement to prevent re-blockage and clopidogrel, a slower-acting but widely used option that’s been the standard for years. Ticagrelor works quicker and more reliably than clopidogrel, which is why it’s now preferred for many post-PCI patients. But neither works alone—they’re often paired with low-dose aspirin for stronger protection. The key is consistency: missing doses can undo months of protection and raise your risk of another heart event.
These drugs aren’t harmless. They can cause bleeding—sometimes serious—if you’re also taking NSAIDs like ibuprofen, or if you’re on other medications that affect how your liver processes them. That’s why you need to talk to your doctor before starting any new supplement or over-the-counter painkiller. Even something as simple as garlic or fish oil can increase bleeding risk when combined with antiplatelet therapy. And if you’re scheduled for surgery or dental work, you might need to pause them temporarily—never stop on your own.
Antiplatelet drugs are most critical for people who’ve had a stent placed, a heart attack, or a stroke. They’re also used in people with peripheral artery disease or certain types of unstable angina. But not everyone needs them. In fact, for healthy people without heart disease, daily aspirin is no longer recommended for prevention. The risks outweigh the benefits. So if you’re unsure whether you should be on one, it’s not about age or fear—it’s about your specific medical history and current condition.
What you’ll find in the posts below are real, practical guides on how these drugs work in the body, how they compare to each other, what to watch out for, and how to avoid dangerous interactions. You’ll learn why ticagrelor is replacing clopidogrel in many cases, how to handle missed doses safely, and which medications can turn a lifesaving drug into a hidden danger. There’s no fluff here—just what you need to know to stay safe and get the most out of your treatment.
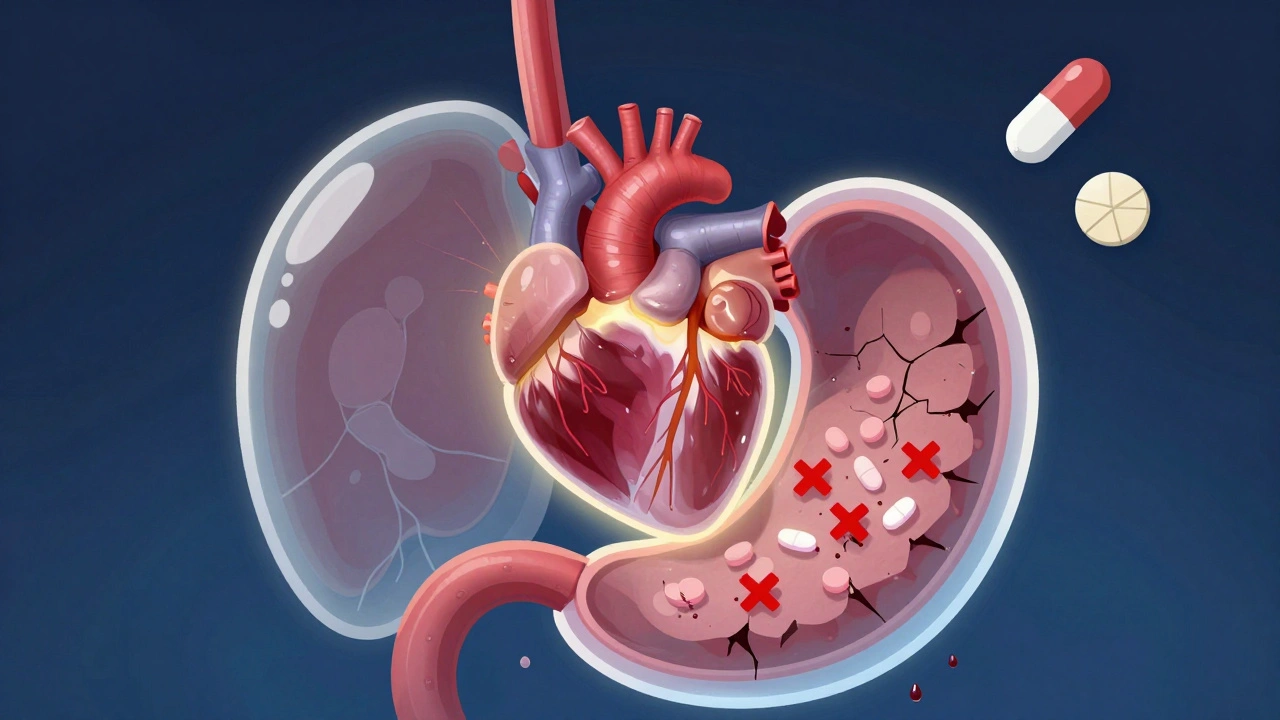
Antiplatelet medications save lives but raise the risk of dangerous stomach bleeding. Learn how to protect your GI tract with PPIs, avoid NSAIDs, and manage risks without stopping your heart meds.
READ