When we talk about GI bleeding risk, the chance of dangerous internal bleeding in the digestive tract from medications, health conditions, or their interactions. Also known as gastrointestinal hemorrhage, it’s not rare—and it’s often preventable if you know what to watch for. This isn’t just about stomach ulcers. It’s about what you take daily—painkillers, heart meds, even supplements—that quietly wear down your gut lining or stop your blood from clotting properly.
NSAIDs, a class of common pain relievers including ibuprofen and naproxen are one of the top culprits. Even if you take them only once in a while, they can cause tiny tears in your stomach or intestines that add up over time. Combine them with anticoagulants, blood thinners like warfarin or apixaban, and the risk doesn’t just go up—it multiplies. Same goes for aspirin, often taken daily for heart protection. Many people don’t realize that even low-dose aspirin can trigger bleeding, especially if they’re older or have a history of ulcers. And it’s not just pills—some herbal supplements like garlic, ginkgo, or fish oil can thin your blood too, quietly adding to the danger.
It’s not always obvious. You might not see blood in your stool right away. Instead, you feel unusually tired, dizzy, or short of breath—signs your body is losing blood slowly. Your stool might turn dark, almost black, like tar. Or you might just feel like something’s "off" without knowing why. These are red flags, not normal aging. The real danger? Doctors often miss it because patients don’t mention their meds unless asked directly. That’s why knowing your own risk matters more than ever.
You’re not alone if you’re on multiple meds. Many people over 65 take five or more drugs daily. Each one adds a layer of risk. But you don’t have to live in fear. You just need to know what’s in your medicine cabinet, who’s prescribing it, and whether any of them are quietly working against your gut health. Below, you’ll find real-world examples of how common medications interact, what to ask your doctor, and how to spot the early signs before it turns into a hospital visit.
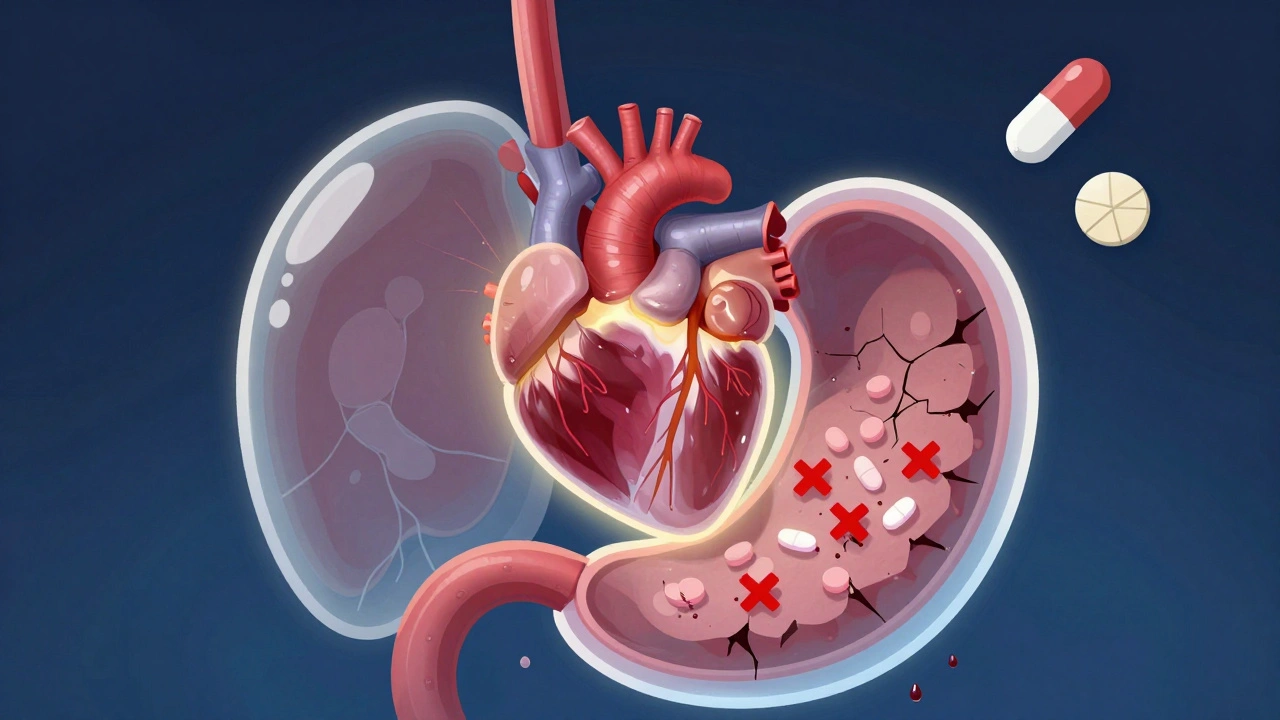
Antiplatelet medications save lives but raise the risk of dangerous stomach bleeding. Learn how to protect your GI tract with PPIs, avoid NSAIDs, and manage risks without stopping your heart meds.
READ