Inflammation is your body's alarm system. When it works short-term, it helps heal cuts and fight infections. When it stays on too long, it damages tissues and fuels conditions like arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), and some lung problems. Knowing the difference between useful inflammation and harmful chronic inflammation changes how you treat it.
Acute inflammation shows up fast: redness, heat, swelling, pain. Think of a sprained ankle or a sore throat. Chronic inflammation is quieter and sneaks up over months or years. It links to autoimmune diseases (like GPA), ongoing infections, obesity, stress, and exposure to irritants such as smoke. Fatigue, unexplained pain, digestive problems, and persistent low fever are common clues you should not ignore.
Different body systems show inflammation in different ways. In the gut, it might be cramps, diarrhea, or bloody stools; that’s where mesalamine helps and may lower colon cancer risk. In the lungs, inflammation causes wheeze and shortness of breath — inhalers like Breztri, Symbicort, and Spiriva target airway inflammation in asthma and COPD. For blood-vessel inflammation, drugs such as baricitinib (a JAK inhibitor) are being explored for conditions like granulomatosis with polyangiitis.
Treatment depends on the cause. Over-the-counter NSAIDs relieve pain and swelling for short-term issues. Steroids work fast for stronger inflammation but carry risks; that’s why many people look into alternatives to Prelone. For chronic conditions, doctors may prescribe targeted therapies — mesalamine for IBD, biologics or JAK inhibitors for autoimmune problems, and inhaled combos for lung disease.
Supplements and lifestyle changes can help reduce low-level inflammation. Eating whole foods, cutting processed sugar, losing extra weight, sleeping well, and moving daily make a big difference. Some people find symptom relief with supplements like English ivy extract for respiratory mucus or L-tryptophan for sleep and mood, but check interactions before you mix anything with prescription drugs.
Buying medicines online? Be careful. Read guides on trusted sellers and how to verify pharmacies before you buy. Our site has practical posts about safe online purchases, alternatives to common drug sources, and how to get real inhalers or nasal sprays safely.
When to see a doctor: get medical help if symptoms are severe, sudden, or getting worse — high fever, trouble breathing, heavy bleeding, or sudden weakness. Also see a specialist if you have ongoing symptoms that affect daily life; early treatment often prevents long-term damage.
Want deeper reads? Check our posts on mesalamine and colon cancer prevention, Prelone alternatives, baricitinib for vasculitis, and inhaler comparisons for asthma and COPD. Those articles give practical, actionable information for common inflammation problems.

Explore how enclomiphene, a testosterone‑boosting SERM, may lower inflammation markers and ease symptoms like joint pain, with evidence, safety tips, and FAQs.
READ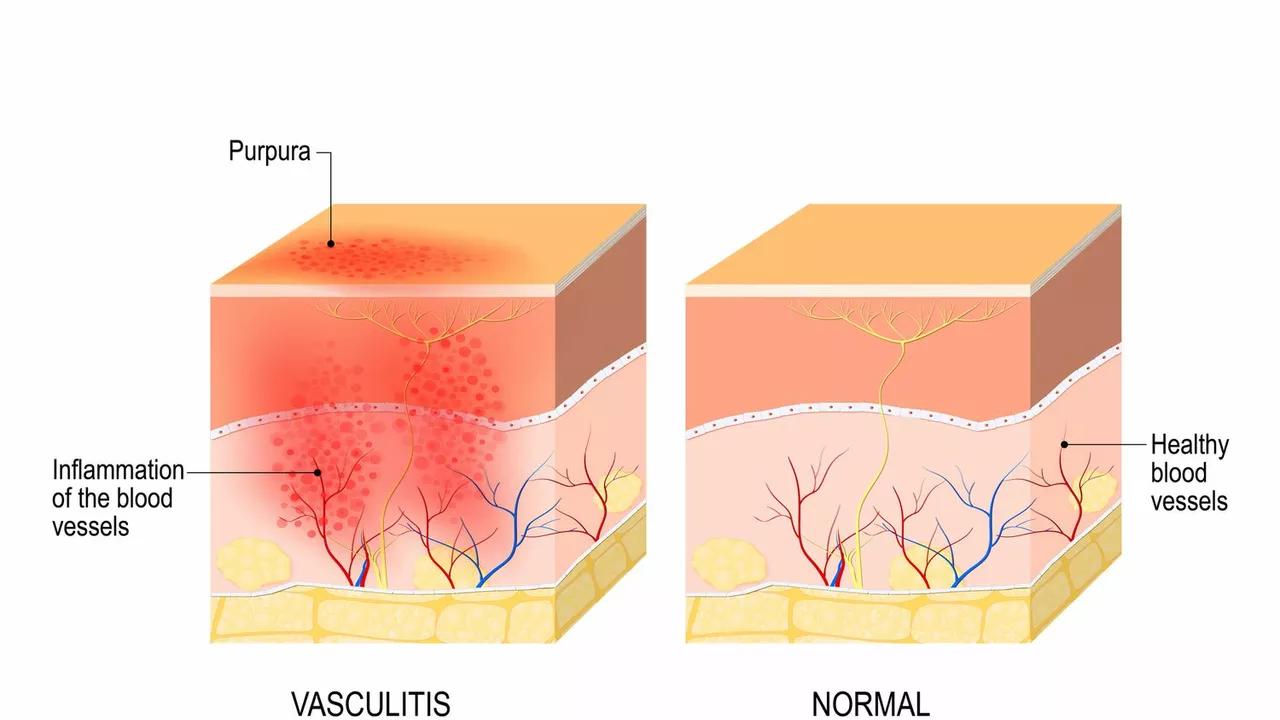
Hey there folks! Let’s dive into an entertaining yet essential health topic - the fascinating link between inflammation and blood clot formation (sounds like a thrilling blockbuster, right?). It's like a dynamic duo, but instead of fighting crime, they're potentially causing health issues. Recent studies show that inflammation is like a sneaky little ringleader, triggering our body to produce more blood clots. These clots are like overzealous party guests, sometimes creating chaos (read: blockages) in our blood vessels. So, take care of your body, folks - it's the only place we have to live, after all!
READ